User Experience and Usability With Example
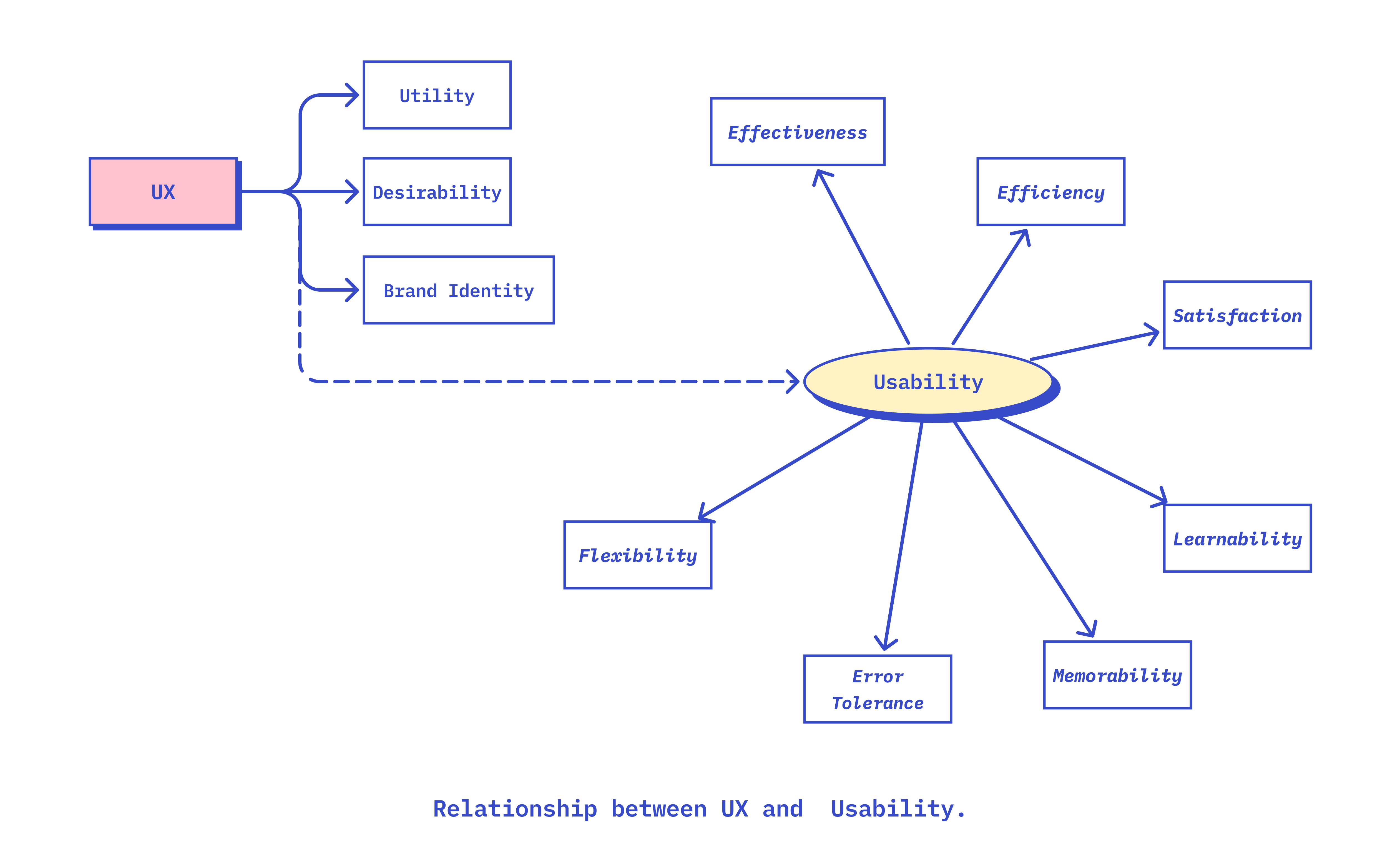
Usability is a crucial component of UX
In today’s digital age, user experience (UX) plays a crucial role in determining the success of a product or service. A well-designed user experience ensures that users can interact with a system seamlessly, leading to higher satisfaction and engagement. At the core of UX lies usability, which defines how efficiently and effectively users can accomplish their goals with minimal frustration. This document explores the key aspects of usability, its importance, and how it contributes to an exceptional user experience.
Introduction to Usability
The ISO defines UX as perceptions and responses generated by the interaction between users and design in an environment. Focusing on the term’s perceptions and responses, we shall explore how these two things are expressed and relate to the human experience. (ISO, 2018)
Usability is a cornerstone of user experience (UX) design. It defines how easily users can interact with a product, system, or service to accomplish their goals. High usability ensures that users can complete tasks effectively, efficiently, and with satisfaction. This section explores the core aspects of usability: effectiveness, efficiency, satisfaction, and additional factors that contribute to a positive user experience.
Note
The ISO Definition of Usability
Usability is a crucial component of UX focusing upon the practical aspects of design, The ISO defines usability as the “extent to which a system, product or service can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a specified context of Use”. (ISO, 2018)
A product with high usability will have a positive user experience since users will be able to use the product without frustration, effectively, and efficiently to achieve the desired objectives.
Key Aspects of Usability
Effectiveness
Definition: Measures how accurately and completely users can achieve their intended goals using the system.
Application: In a word processor, effectiveness might be judged by how well users can create, edit, and save documents without errors.
Indicators:
- Accuracy: Precision in users’ actions and task outcomes.
- Task Completion Rate: Percentage of successfully completed tasks.
- Error Rate: Frequency and severity of user errors.
Efficiency
Definition: Measures the speed and ease with which users can complete tasks after learning the system.
Application: For an e-commerce site, efficiency is reflected in how quickly a user can locate a product, add it to the cart, and check out.
Indicators:
- Task Time: Time required to complete a task.
- Number of Steps: Fewer steps generally indicate higher efficiency.
- Resource Utilization: The ease of completing goals with minimal effort (e.g., fewer clicks, reduced scrolling).
Satisfaction
Definition: Users subjective enjoyment and fulfillment from interacting with the product.
Application: A user-friendly app that is intuitive and visually appealing can increase user satisfaction.
Indicators:
- User Feedback: Insights from surveys or focus groups.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures likelihood of users recommending the product.
- Emotional Engagement: Users’ enjoyment, trust, and overall emotional connection to the product.
Learnability
Definition: The ease with which new users can learn the system, is crucial for complex applications.
Application: An intuitive interface in a software application makes it easy for new users to understand and start using key features.
Indicators:
- Onboarding Time: Time needed for users to become proficient.
- User Errors: Types and frequency of errors by new users.
- Availability of Training: Tutorials or guides to facilitate learning.
Memorability
Definition: Measures how easily users can remember how to use the product after a period of not using it.
Application: An infrequently used travel booking site should be easy to navigate without extensive relearning.
Indicators:
- Recall Rate: Users’ ability to remember key tasks after a break.
- Relearning Time: Time required to regain proficiency.
Error Tolerance
Definition: The system’s ability to prevent errors and help users recover from them.
Application: A form-filling app that highlights incomplete fields and offers error correction suggestions.
Indicators:
- Error Prevention: Features that reduce the likelihood of errors, such as input validation.
- Error Recovery: Ease of correcting mistakes, with clear error messages.
- Minimal Consequences: Limiting negative impacts from errors (e.g., data preservation).
Flexibility
Definition: The system’s adaptability to accommodate different user needs and preferences.
Application: A text editor that allows customization of layout, fonts, and shortcuts.
Indicators:
- Customization Options: Ability to personalize interface and workflows.
- Accessibility: Features like screen readers and adjustable font sizes.
- Multiple Interaction Methods: Supports various input modes (e.g., voice, touch, keyboard).
Usability, a critical element of UX, encompasses effectiveness, efficiency, satisfaction, learnability, memorability, error tolerance, and flexibility. Products with high usability not only attract more users but also enhance satisfaction and encourage continued use. To demonstrate these aspects in action, consider the following mobile banking app scenario.
Example Scenario: Mobile Banking App
Key Usability Aspects in a Mobile Banking App
1. Effectiveness
Design Example: The app enables users to transfer money, pay bills, and check balances.
Indicators: Features like task completion accuracy, error prevention (confirmation screens), and input masks enhance effectiveness.
2. Efficiency
Design Example: The app’s quick actions allow users to complete common tasks rapidly.
Indicators: Fewer steps for frequently used actions, and optimized performance on various devices.
3. Satisfaction
Design Example: The app provides a seamless and visually appealing experience.
Indicators: Positive user feedback, Net Promoter Score, and options for customization foster satisfaction.
4. Learnability
Design Example: The app offers a simple tutorial for new users.
Indicators: Easy-to-navigate interface and step-by-step onboarding enhance learnability.
5. Memorability
Design Example: Users can easily navigate familiar features after a break in usage.
Indicators: Consistent navigation and simple design support memorability.
6. Error Tolerance
Design Example: Real-time input validation and undo options enhance error tolerance.
Indicators: Clear error messages and easy correction options improve user confidence.
7. Flexibility
Design Example: The app includes accessibility options and customizable layouts.
Indicators: Multiple input methods and customization support flexibility.
The design of this app exemplifies how prioritizing usability leads to a high-quality user experience, one that boosts satisfaction, repeat usage, and positive recommendations. By addressing each usability factor, the product remains functional and user-centric, increasing its impact and success.
Conclusion
Usability is a key component of user experience, focusing on effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction while incorporating learnability, memorability, error tolerance, and flexibility. High usability ensures that users can achieve their goals smoothly and without frustration, creating a positive experience that encourages continued use.
In the rapidly evolving world of technology and digital interactions, usability remains a fundamental pillar of design. Products that prioritize usability not only attract more users but also retain them by fostering ease of use, trust, and satisfaction.
By integrating usability principles into design processes, businesses can develop intuitive, accessible, and user-friendly products that stand out in the competitive landscape. Ensuring usability is not just an advantage—it is a necessity in delivering exceptional user experiences that drive engagement and long-term success.

Leave a Reply